About Paediatric Orthopaedics
Paediatric Orthopaedics disorders and injuries range from minor fractures to more severe conditions requiring extensive treatment and rehabilitation.
Paediatric orthopaedic disorders and injuries can be very concerning for both parents and children. These conditions can range in severity from minor fractures to more severe injuries that may require extensive treatment and rehabilitation. The purpose of this article is to provide an overview of the most common orthopaedic conditions and injuries experienced by children. These include fractures, dislocations, clubfoot, flat foot, bowlegs, knock knees, hip disorders, infections of bones and soft tissues, cerebral palsy, and gait abnormalities.
However, the elbow is also prone to various disorders and injuries, which can cause pain, discomfort, and difficulty performing daily activities. In this article, we will discuss three common types of elbow disorders and injuries: fractures and dislocations, osteoarthritis, and soft tissue injuries.

Fractures or Dislocations of Upper & Lower Limbs
Upper and lower limb fractures and dislocations are common childhood injuries. Fractures range from simple breaks that do not disrupt bone alignment to more complex fractures that require surgery. Dislocations occur when bones in a joint are forced out of place. Falls, sports injuries, or other traumatic events can cause dislocations and fractures. The affected limb may be immobilised with a cast or splint, treated with physical therapy, or operated on.
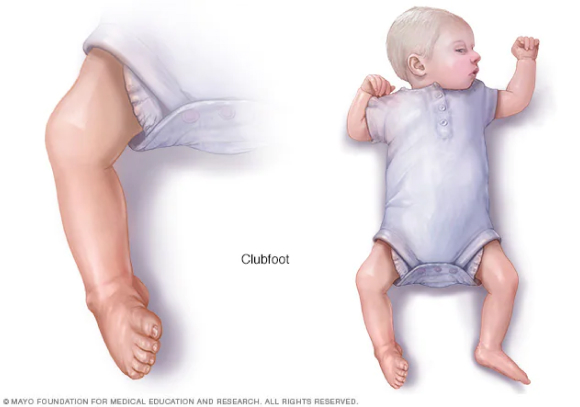
Clubfoot / Congenital Talipes Equinovarus (CTEV)
Congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV) is a birth defect that affects the feet and ankles. Clubfoot causes the feet to be turned inward and downward, making walking difficult. The exact cause of clubfoot is unknown, but genetics and the environment are suspected. Casts, braces, and physical therapy are used to stretch and reposition the affected foot in clubfoot treatment slowly. Severe cases of clubfoot may require surgery.
Flat Foot
Pes planus refers to a condition where the foot’s arch collapses, causing the entire sole of the foot to contact the ground. Congenital flat feet (present at birth) or acquired flat feet. Children with flat feet may experience pain, fatigue, and difficulty standing or walking for long periods. In some cases, surgery is needed to treat flat feet. Orthotic inserts, physical therapy, or both may be used.
Bowlegs and Knock Knees
Bowlegs and knock knees are conditions where the legs are curved rather than straight. Bowlegs, or genu varum, occur when the legs curve outward and knock knees, or genu valgum, occur when they curve inward. These conditions can be present at birth or develop later. As a child grows, bowlegs and knock knees usually resolve independently. It may be necessary to treat severe cases to correct leg alignment.

Hip Disorders
The hip joint plays an instrumental role in walking and other weight-bearing activities for children. In children, hip dysplasia is a condition in which the hip joint is not properly formed, and developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) is a condition in which the hip joint is unstable. These conditions can cause pain, difficulty walking, and leg and hip deformities. Braces, physical therapy, or surgery may be used to treat hip disorders.
Bone & Soft Tissue Infections
Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis are serious conditions in children. Septic arthritis is an infection of a joint, while osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone. These conditions cause fever, pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected limb. Antibiotics, surgical drainage, and surgery to remove infected tissue are often used to treat bone and soft tissue infections.
Cerebral Palsy
Movement and muscle tone are affected by cerebral palsy. Often before or during birth, it results from abnormal brain development. Movement, coordination, and muscle control may be difficult for children with cerebral palsy. Cerebral palsy may be treated with physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and medication.
Gait Abnormalities / Limping
Several factors can affect a child's gait, including injuries, neurological conditions, and structural abnormalities. Gait abnormalities can make children limp or have difficulty walking. Orthotic devices, physical therapy, and surgery can all be used to treat gait abnormalities.

Paediatric orthopaedic disorders and injuries range from minor fractures to more severe conditions requiring extensive treatment and rehabilitation. The most favourable outcome comes from early diagnosis and treatment.
Visit SJMC's Orthopaedic & Spine department if you have concerns about your child's musculoskeletal health.
Let our team of specialists help your child regain health and mobility.

